Key Takeaways
- 24VAC Control Architecture: Zone panels distribute power through dedicated terminals (R, C, W, Y, G, O/B) with zone-specific damper controls requiring careful wire routing and transformer sizing
- Communication Protocols Matter: From basic relay logic to RS-485 serial communication, understanding how thermostats talk to zone panels determines system compatibility
- Smart Thermostat Challenges: The C-wire requirement and power-stealing circuits create integration headaches that require creative solutions or equipment upgrades
- Wireless Isn’t Always Better: While RF systems offer installation flexibility, interference issues and battery management can create more problems than traditional wired solutions
Welcome to the reality of zone control integration – where thermostats, dampers, and control panels must work in perfect harmony, or the whole system falls apart.
The Foundation: Understanding Zone Control Architecture
Every zone control system starts with the same basic premise: distribute conditioned air where it’s needed, when it’s needed. But the devil is in the details of how these components communicate.
The zone control panel serves as the brain, managing all communication between thermostats, dampers, and HVAC equipment. It’s essentially a sophisticated relay system that takes thermostat calls and translates them into equipment operation and damper positioning. Understanding how HVAC control boards work helps you diagnose whether the panel itself is the problem or if the issue lies in the peripheral components.
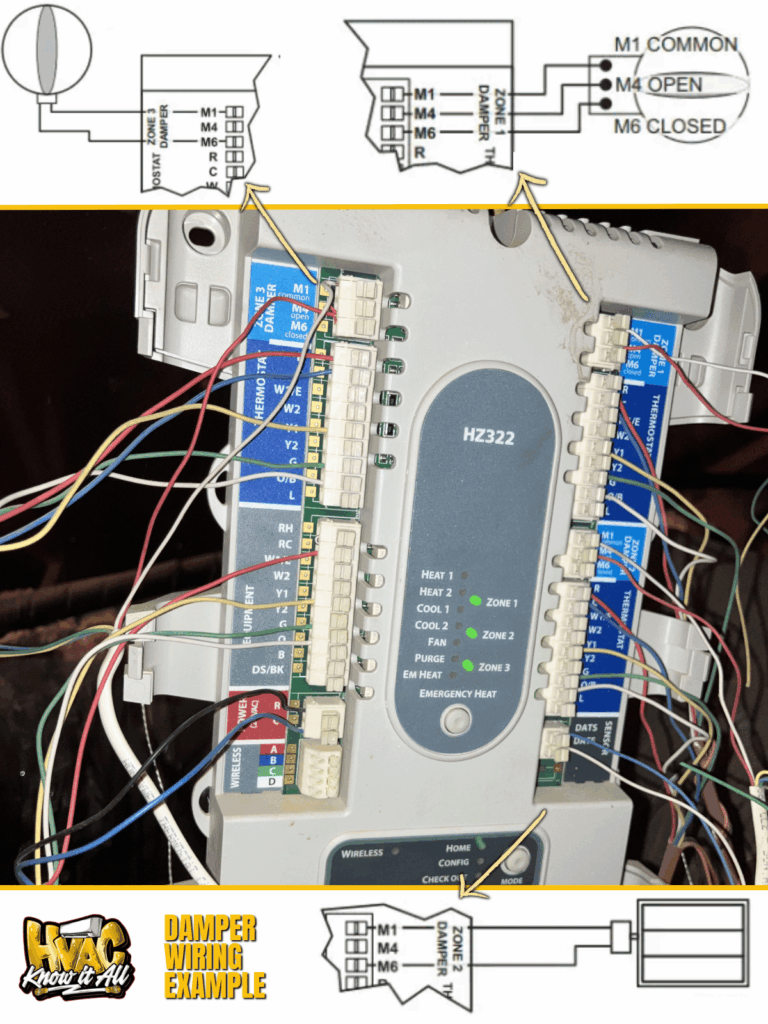
As you know, tandard 24VAC control connections include:
- R (hot) and C (common) for power
- W1/W2 for heating stages
- Y1/Y2 for cooling stages
- G for fan operation
- O/B for heat pump reversing valve
But here’s where it gets interesting – zone-specific terminals like M1 (damper common), M4 (power-open), and M6 (power-close) provide individual damper control while maintaining electrical isolation between zones.
Wiring: The Backbone of Reliable Zone Control
Proper wiring isn’t just about making connections – it’s about creating a reliable communication network. I’ve seen too many callbacks caused by undersized transformers or improper wire routing. Understanding how to read wiring diagrams is essential for successful zone control installation.
Start with transformer sizing. Calculate your load:
- Panel draw: 10-14VA
- Per-zone damper: 2-8VA
- Thermostat loads: 1-3VA
For a 4-zone system, you’re looking at minimum 40VA, but I always spec 60VA for headroom. This dedicated transformer should be separate from your equipment power to prevent voltage fluctuations during cycling that can scramble your zone panel’s tiny brain.
Wire routing matters more than most techs realize. Run individual 18/5 or 18/8 cables in a hub-and-spoke pattern from the panel to each zone. Keep runs under 250 feet and maintain at least 6-inch separation from line voltage wiring. Those induced voltages from parallel high-voltage runs can create phantom calls that’ll drive you crazy during troubleshooting.
When you need to ensure reliable wire connections, watch this video on properly preparing wires for twist-on connectors – a skill critical for zone control wiring.
For technicians working with more complex installations, understanding BMS network architecture provides insight into how commercial systems handle similar communication challenges on a larger scale.
Damper Integration: More Than Just Open and Close
Damper actuators are where electrical signals become mechanical action. Selection depends on torque requirements, control methods, and what your zone panel can actually support. When working with economizers, check out this comprehensive guide to economizer damper operation for insights into damper control logic.
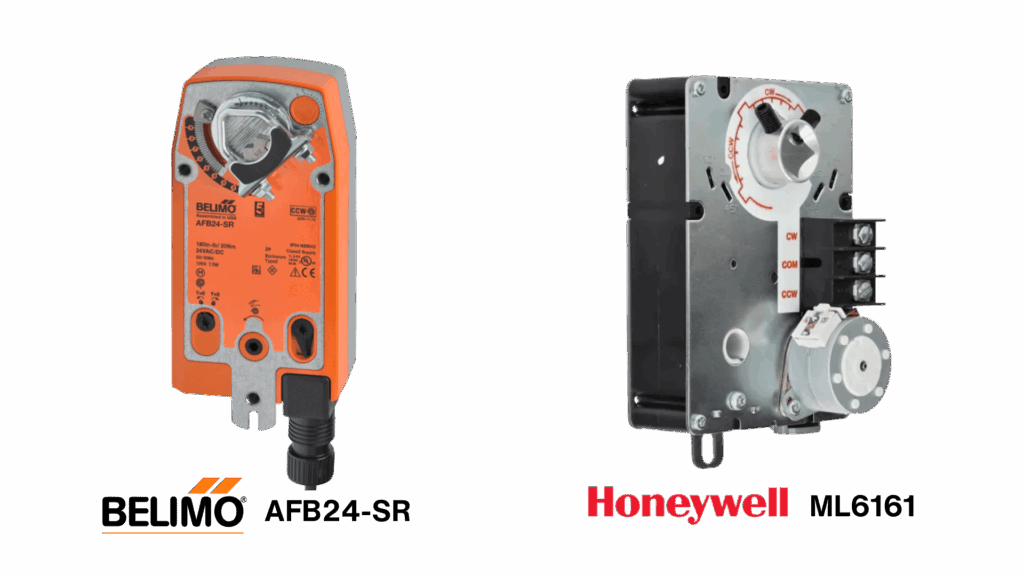
Spring-return actuators dominate residential applications for good reason – they fail safe. Models like the Belimo AFB24-SR deliver 180 in-lb torque with modulating 2-10VDC control, while lighter options like the Honeywell ML6161 provide 35 in-lb for smaller dampers.
Control signal compatibility determines your options:
- Basic 24VAC On/Off: Simple two-position operation through SPDT relay contacts. Reliable but lacks finesse.
- Proportional 2-10VDC: Industry standard for modulating control. 2V = closed, 10V = open, with fail-safe below 2V. This is what you want for variable-speed equipment integration.
- Floating Point: Three-wire configuration with separate open/close signals. Great for incremental adjustments but requires compatible zone panels.
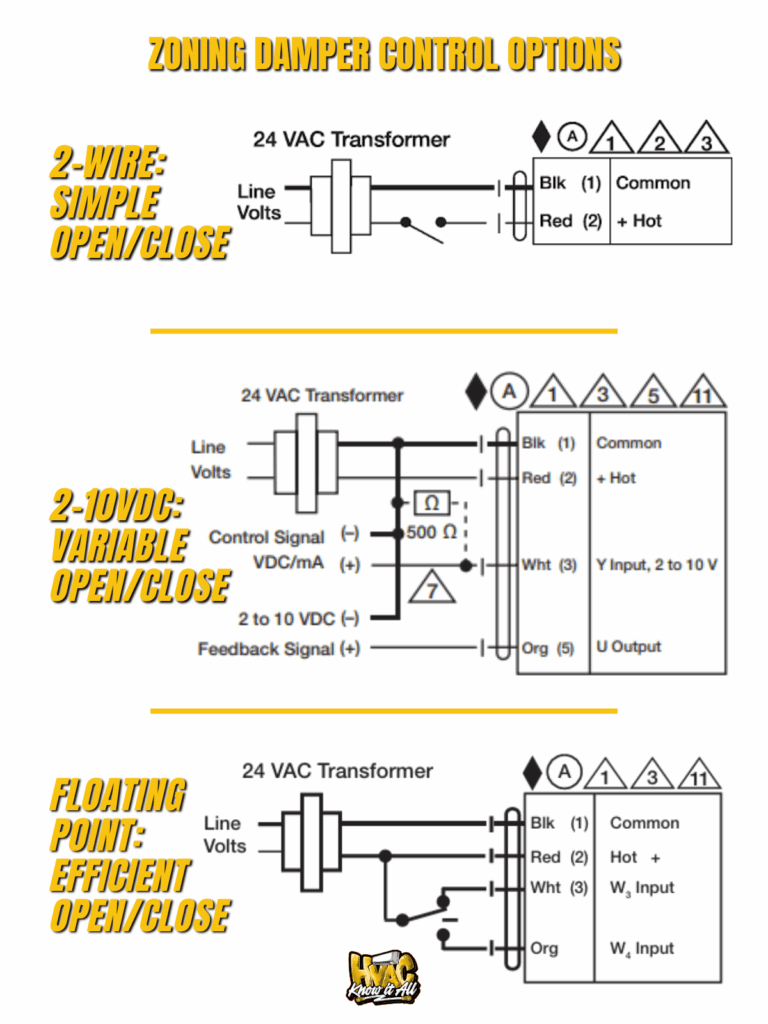
Don’t overlook timing specs. Standard actuators take 90 seconds to 7 minutes for full rotation. Faster isn’t always better – rapid movement can cause air hammer in tight ductwork.
For troubleshooting damper actuator issues, watch this video on testing damper actuator spring return rotation. Also, when economizer dampers get stuck, see this troubleshooting video on fresh air dampers stuck open.
The Smart Thermostat Integration Challenge
Smart thermostat integration with zone controls presents unique electrical challenges beyond simple C-wire additions. The zone panel’s internal architecture – whether relay-based, triac-controlled, or hybrid – determines compatibility more than any other factor.
Modern zone panels use triacs for silent operation, but these solid-state switches leak current – typically 3-5mA. Smart thermostats interpret this leakage as a valid call signal, creating feedback loops that manifest as random zone activation or equipment short-cycling. The problem compounds when multiple smart stats share a common transformer through the zone panel.
Your mitigation strategies depend on the panel generation:
- Pre-2010 panels: Relay-based switching tolerates power-stealing but requires RC/RH jumper removal to prevent transformer coupling
- 2010-2018 panels: Hybrid designs need careful voltage monitoring – check for >20VAC on inactive terminals
- Post-2018 panels: Most include dedicated C terminals per zone, but verify current capacity (minimum 100mA per stat)
The Fast-Stat ecosystem and Copeland’s EIM aren’t just workarounds – they’re engineered solutions that maintain electrical isolation while providing necessary power. When zone panels lack individual C terminals, these tools prevent the ground loops and voltage imbalances that cause erratic operation.
Communication Protocols: Speaking the Same Language
Digital protocols have revolutionized zone control capabilities, but they’ve also created compatibility nightmares.
Carrier’s ABCD Bus: Uses RS-485 serial communication at 38,400 baud. Terminals A and B handle data while C and D distribute power. Great for equipment integration, terrible for universal compatibility. If you’re not all-in on Carrier, skip it.
Honeywell’s RedLINK: Operating in the 902-928 MHz band, it penetrates building materials better than WiFi. The HZ432 panel supports four wireless thermostats with automatic configuration. Range is impressive, but at $200+ per thermostat, it’s not cheap.
Universal Protocols: ModBus RTU and BACnet MS/TP enable commercial integration but require serious technical knowledge. If you’re comfortable with BMS control fundamentals, these open standards offer maximum flexibility.
Troubleshooting Integration Issues
When zones stop responding, systematic diagnosis beats parts replacement every time. For comprehensive troubleshooting fundamentals, check out this general guide to HVAC troubleshooting.
Start with the basics:
- Verify 24VAC at the zone panel and each thermostat
- Check transformer VA rating – inadequate power causes intermittent operation
- Test damper actuators independently using a 24VAC source
- Measure control signals during calls for heating/cooling
Common failure points often encountered in the field:
- Burned relay contacts from excessive damper motor current – check continuity on switches and contactors
- Failed triacs in electronic zone panels from voltage spikes
- Corroded connections causing high resistance
- RF interference in wireless systems from new electronics
Related Video: Troubleshooting Lennox RTU control boards and low voltage wiring.
For dampers specifically, check for mechanical binding before condemning the actuator – you may find everything from dead mice to construction debris jamming damper blades. A $500 actuator replacement won’t fix a mechanical obstruction.
Variable-Speed Equipment: The Integration Wild Card
Variable-speed systems require zone controls that can modulate based on demand rather than simple on/off operation. Not all zone panels can handle this. Understanding how ECM motors work is crucial for proper integration.
ECM motors need specific control interfaces. Universal panels may provide basic compatibility through fan relay terminals but lack sophisticated modulation. This is where manufacturer-specific systems like Carrier Infinity or Trane ComfortLink shine – they’re built for variable-speed integration from the ground up.
The converged systems approach that pairs inverter heat pumps with traditional air handlers represents the future of zoning. For insights on multi-zone ductless systems, watch this video on ductless heat pump zoning tips.
Moving Forward with Zone Control
Zone control integration isn’t getting simpler. As equipment becomes more sophisticated and homeowners demand smart home integration, the technical requirements keep climbing. But understanding the fundamentals – proper wiring, appropriate component selection, and systematic troubleshooting – remains the foundation of successful installations.
Whether you’re retrofitting an older system or installing cutting-edge equipment, the principles stay the same: ensure adequate power, maintain signal integrity, and verify compatibility before you start wiring.
PARTING TIP:
Mastering zone control systems takes your expertise to the next level. Property.com’s ‘Know Before You Go‘ tool helps you identify homes with complex HVAC systems before you arrive, allowing you to bring the right zone control components and expertise to every call. From spotting multi-story homes perfect for zoning retrofits to understanding previous HVAC work, Property.com gives you the intelligence edge that sets professionals apart.
Whether you require installation, repair, or maintenance, our technicians will assist you with top-quality service at any time of the day or night. Take comfort in knowing your indoor air quality is the best it can be with MOE heating & cooling services Ontario's solution for heating, air conditioning, and ventilation that’s cooler than the rest.
Contact us to schedule a visit. Our qualified team of technicians, are always ready to help you and guide you for heating and cooling issues. Weather you want to replace an old furnace or install a brand new air conditioner, we are here to help you. Our main office is at Kitchener but we can service most of Ontario's cities
Source link